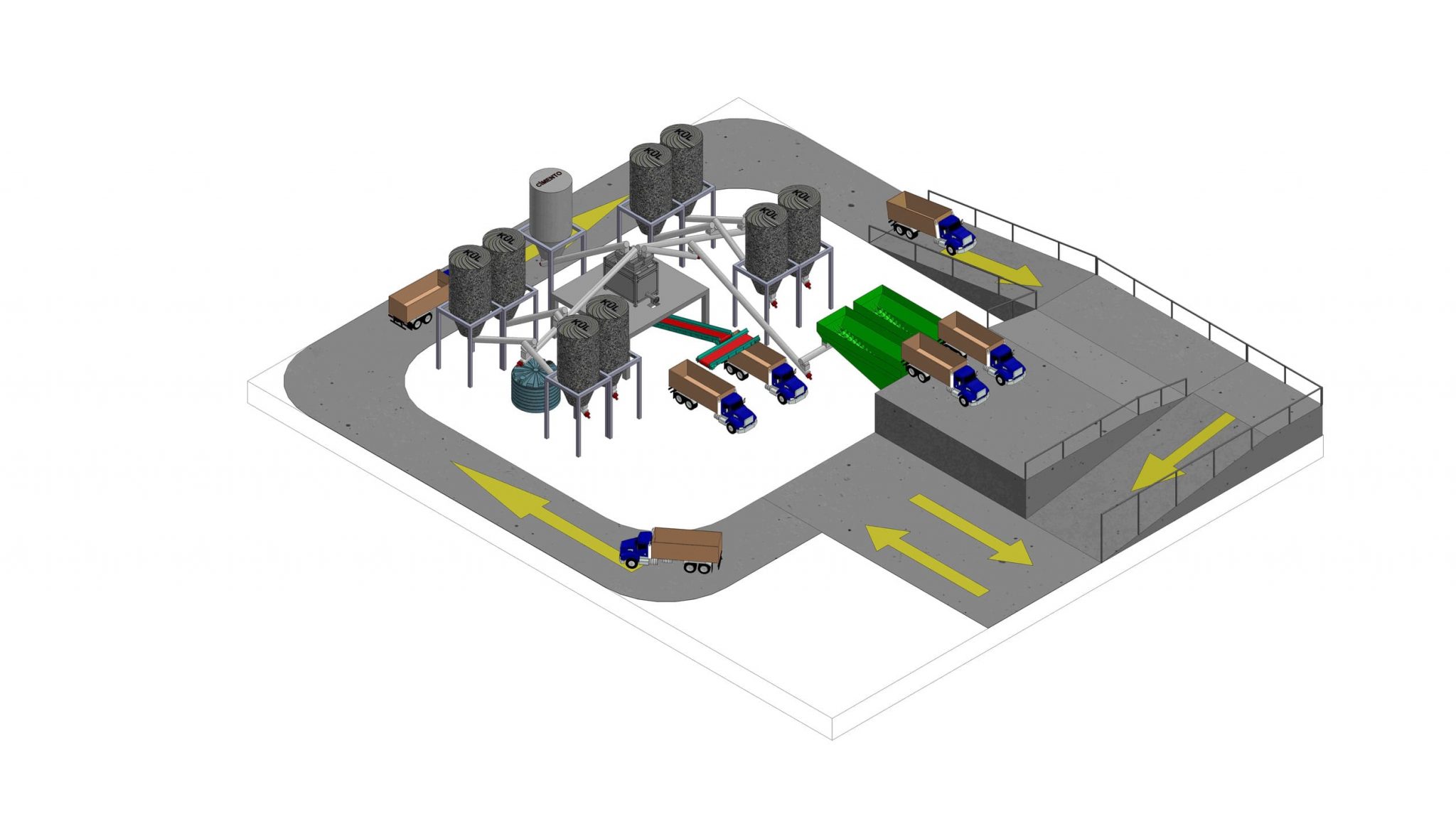
Stabilization and Solidification Facilities are an essential part of modular waste-to-value systems, designed to safely treat hazardous wastes by altering their physical and chemical properties. These processes reduce toxicity and prevent leachability, ensuring secure storage and minimizing environmental impact. Integrated into comprehensive waste management workflows, these facilities protect human health, support regulatory compliance, and contribute to responsible, resource-efficient waste handling across the entire system.